To understand a bogon IP address, we first need to know how the allocation and management of IP addresses works.
With so many internet users, how come each one has a unique IP address? Doesn’t the IP address pool run out of IPs to assign to new devices? Yes, the address space can run out of addresses, which is why there are two addressing protocols: IPv4 and IPv6.
Both these address spaces have a portion of unallocated addresses, also called bogon IP addresses.
As new users and devices join the Internet, some IPs from the bogon IP address space become legitimate. The responsible authority, IANA, assigns these addresses to the new devices and users.
It might seem a little confusing but don’t worry. In this article, we’ll explain in detail what is a Bogon IP address and how to detect it. So, without further ado, let’s start!

Table of Contents
What Is a Bogon IP Address?
A bogon IP address meaning is simple. It is an IP address from reserved or unallocated space that should not appear on the public Internet.
The term “bogon” originates from “bogus,” meaning false or non-genuine. These addresses are part of bogon space, which includes both unallocated and private IP addresses.
Bad actors often use Bogon IPs in their attacks because these addresses are untraceable.
IANA, the authority overseeing IP allocations, does not assign bogon IPs for use on the public Internet. However, misconfigurations or malicious actors often cause them to appear on public networks.
Misassigned bogon IPs can lead to routing issues and potential security threats if not managed properly.
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and network administrators actively filter out bogon IPs to prevent unauthorized access and attacks.
Network administrators refer to this process as bogon filtering. It uses router access control lists (ACLs) or Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) blackholing to block traffic from the bogon list.
It’s important to note that the bogon list keeps updating as IANA assigns new address space to ISPs.
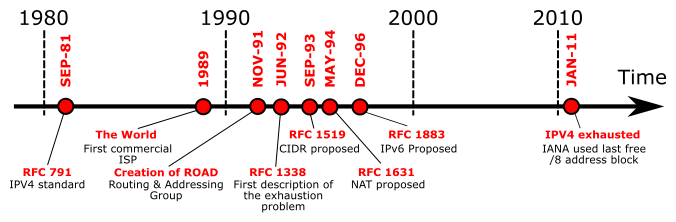
By 2011, IANA had assigned all unallocated IP addresses with which the IPv4 bogon space depleted. Since then, the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) has advised network administrators to stop filtering bogons from the IPv4 address pool.
2 Major Security Risks of Bogons
While not legitimate for use on the public internet, bogon IP addresses still pose significant security threats. The two major cyber-attacks that use bogons are:

1. Distributed Denial of Service Attacks (DDoS)
DDoS attacks flood a target device with excessive traffic to overwhelm its resources and disrupt services. The motive is to exhaust the target system’s bandwidth, which leads to service outages and financial losses.
Attackers often use Bogon IP addresses to mask their origin. They’re difficult to trace because there is no information about them.
2. TCP SYN Scanning
TCP SYN scanning identifies open ports on a target system. Attackers send SYN packets to various ports to seek responses that indicate available vulnerabilities to exploit later.
They use Bogon IP addresses to conduct these scans anonymously, as these are not easily traceable back to them.
How To Determine if the IP Address Is a Bogon IP
Detecting a Bogon IP address involves a process called Bogon filtering. This method ensures that only legitimate IP addresses access the public Internet.
First, networks use a bogon list, which contains all reserved and unspecified IP addresses. This list regularly changes, and you can source it from organizations like Team Cymru.
Next, network administrators implement access control lists (ACLs) based on the bogon list. These ACLs filter out traffic originating from or destined for Bogon IP addresses.
Firewalls and routers use these ACLs to block traffic from Bogon IP addresses. Regular updates to the bogon list ensure the accuracy of these filters. Automated tools can also help update and maintain these lists.
The ideal solution is to use an IP that dynamically blocks and unblocks bogons as the list changes.
Apart from this, monitoring tools and intrusion detection systems can identify and alert administrators to Bogon IP activity.
This helps prevent unauthorized access and potential security threats like DDoS attacks.
Once you have detected a bogon IP address, the next step is to geolocate it. But is it even possible? If yes, then how to find a bogon IP address’s location? Let’s find out.
How To Find a Bogon IP Address Location
Finding the location of a Bogon IP address is impossible. Bogon IP addresses are from unallocated or reserved IP ranges.
These addresses lack geographical assignments and don’t have a physical location.
Geolocation databases map and allocate IP addresses to physical locations. Since a Bogon IP address is an unspecified address, it does not appear in these databases.
Therefore, attempting to geolocate these IPs returns no location information. Instead, geolocation services display a message informing the detection of a bogon IP address.
If a network detects a Bogon IP address, it should treat it as an unspecified address and block it. This action prevents potential misuse or security risks.

IPv4 and IPv6 IP Addresses in the Bogon List
While the bogon list keeps changing, here are some addresses that make up the bogon list. Keep in mind that this is an incomplete list.
IPv4 Bogon IP Addresses
- Private IP Ranges: 10.0.0.0/8, 172.16.0.0/12, 192.168.0.0/16
- Link-Local: 169.254.0.0/16
- Multicast: 224.0.0.0/4
- Carrier-grade NAT: 100.64.0.0/10
- Loopback: 127.0.0.0/8
- and others
IPv6 Bogon IP Addresses
- Link-Local: fe80::/10
- Multicast: ff00::/8
- Unspecified: ::/128
- 6to4 bogon addresses
- Teredo bogons
- and others
The next question is, does email forwarding involve a bogon IP address? Here’s an answer.

Does Email Forwarding Involve Bogon IP Address?
Email forwarding does not usually involve Bogon IP addresses.
In email forwarding, a mail server receives an email and forwards it to another address. The source IP address and destination IP address inside the email header should be valid and allocated.
Using a Bogon IP address in this process could result in delivery failures.
Mail servers check IP addresses to ensure they are legitimate. This prevents using unallocated or private IP addresses in public email transactions.
Use geoPlugin to Filter IPs!
Filtering bogon IP addresses is crucial for network security. By blocking traffic from the bogon list, administrators can protect their networks from unauthorized access and malicious activities.
But this is only possible if you’re vigilant about network security. You should use APIs to monitor and investigate IPs interacting with your servers and preemptively block attacks. geoPlugin is a geolocation service provider that can be highly useful in this regard.
geoPlugin’s API can process IP addresses and extract a long list of details about them. Using geoPlugin services, you can also identify whether the IP address is a bogon IP address.
So sign up for geoPlugin’s easy-to-use API today and fend off bogon-related cyber attacks.